Git and Github for Mappers: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (118 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
There are other cloud-based hosting services for Git repositories such as [https://about.gitlab.com/ Gitlab] and [https://bitbucket.org/ Bitbucket] which offer similar functionality. | There are other cloud-based hosting services for Git repositories such as [https://about.gitlab.com/ Gitlab] and [https://bitbucket.org/ Bitbucket] which offer similar functionality. | ||
=== What is a Git repository? === | |||
A Git repository is a versioned collection of related files that (usually) make up a software application, or part of an application stack. In the context of this tutorial, our Git repository will only include the TDM fan mission files and nothing else. | |||
When you create a repository on Github however, a whole bunch of other features related to the repository become available to you. | |||
=== Benefits === | === Benefits === | ||
| Line 23: | Line 28: | ||
Using Github has the following major benefits to the mapper: | Using Github has the following major benefits to the mapper: | ||
* '''Versioning and history'''. Easily tell what's changed in your project, and when. Also comes in handy for fixing mistakes. | * '''Versioning and history'''. Easily tell what's changed in your project, and when. Also comes in handy for fixing mistakes. | ||
* '''Data loss protection'''. Your FM code stays in the cloud, protected by a | * '''Data loss protection'''. Your FM code stays in the cloud, protected by a resilient hosting platform owned and operated by Microsoft. There is almost zero risk your project can be lost | ||
* '''Easier collaboration'''. If you work with others, using Github has many benefits that will be expanded upon in this article (for example, one-click synchronization of FM files for collaborators instead of passing .pk4 files around) | * '''Easier collaboration'''. If you work with others, using Github has many benefits that will be expanded upon in this article (for example, one-click synchronization of FM files for collaborators instead of passing .pk4 files around). See [[Git_and_Github_for_Mappers#Implications|'''implications''']] for more details. | ||
* '''Discovery and | * '''Discovery and visibility'''. Your FM code will be publicly available in the same place for the foreseeable future (if you choose for it to be). This makes it very easy to share, for others to find on their own, or just read later if you want to remember how you did something. Want to show someone how you wrote that script? Just [https://github.com/thedarkmodcommunity/hits1/blob/main/maps/man2.script '''send them a link!''']. Can't find that .ogg file you used for secrets anywhere? [https://github.com/thedarkmodcommunity/hits1/blob/main/sound/map_specific/secret.ogg '''Just grab it!'''] | ||
* '''It's free!'''. See list of features available [https://github.com/pricing#compare-features here]. | |||
Other less important features that I have found useful: | Other less important features that I have found useful: | ||
* A project board where you can create and manage work and track progress (similar to a Kanban board). | * A project board where you can create and manage work and track progress (similar to a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kanban_board Kanban board]). | ||
* a built-in Wiki for your project. Useful for fleshing out story ideas. | * a built-in Wiki for your project. Useful for fleshing out story ideas. | ||
* the ability to create release artifacts. For example, you can package up your FM as a .pk4 and upload it to the project, providing a public place for others to download | * the ability to create release artifacts. For example, you can package up your FM as a .pk4 and upload it to the project, providing a public place for others to download | ||
| Line 34: | Line 40: | ||
* an image diff viewer | * an image diff viewer | ||
It is important to note that all the above features are available in the context of your FM project. | It is important to note that all the above features are available in the context of your FM project. Everything is in one place. | ||
=== Why use a VCS and not just Google Drive/Dropbox? === | === Why use a VCS and not just Google Drive/Dropbox? === | ||
Although storing your files on cloud storage protects them against data loss, there are some drawbacks: | Although storing your files on cloud storage protects them against data loss, there are some drawbacks: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ | |||
|- | |||
! Feature !! Git/Github !! Traditional Cloud Storage | |||
|- | |||
| Resilient Cloud Hosting || yes || yes | |||
|- | |||
| Ease of file transfer || one or two clicks to synchronize, no manual compression or extracting required || manual zipping/extracting, uploading/downloading | |||
|- | |||
| Versioning || built-in || may be able to version files (e.g. Google Drive, but not a VCS and not practical unless packaged in a single file) | |||
|- | |||
| File visibility || all files easily browseable || no, especially if packaged (e.g. .pk4) | |||
|- | |||
| Discovery || public links, discoverable by anyone || no, private accounts, non-discoverable public links, may or may not be available | |||
|- | |||
| Online Collaboration || yes, via pull request || no | |||
|} | |||
== Tutorial == | == Tutorial == | ||
The scope of this tutorial will: | The scope of this tutorial will: | ||
* focus on Windows users only | * focus on Windows users only (although Linux users can follow along just fine - Git and VS Code are available for Linux as well) | ||
* include the use of Visual Studio Code. The reason for using this is to demonstrate that '''most Git interaction can be done without the use of the command line'''. If you have another preferred editor, check if it has a Git plugin and you can use that instead. | * include the use of Visual Studio Code. The reason for using this is to demonstrate (using its Git plugin) that '''most Git interaction can be done without the use of the command line'''. If you have another preferred editor, check if it has a Git plugin and you can use that instead. | ||
=== Tool Setup === | === Tool Setup === | ||
| Line 60: | Line 79: | ||
==== First-time Git Setup ==== | ==== First-time Git Setup ==== | ||
After installing Git, open a command prompt and type the following. You can put whatever you want for the values | After installing Git, open a command prompt and type the following. You can put whatever you want for the values (enclose user.name in double quotes if it has a space) | ||
git config --global user.name <your user name here> | git config --global user.name <your user name here> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 96: | ||
==== Create a new repository ==== | ==== Create a new repository ==== | ||
'''NOTE:''' if you have an existing FM that you want to add to Github now, see [[Git_and_Github_for_Mappers#Adding_an_Existing_FM_to_Github|'''Adding an Existing FM to Github''']]. | |||
Log into your Github account and create a new repository. Depending if this is this first time you've logged in or not, you may see different screens. Either way, you will arrive at this screen: | Log into your Github account and create a new repository. Depending if this is this first time you've logged in or not, you may see different screens. Either way, you will arrive at this screen: | ||
| Line 82: | Line 103: | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
The 'Repository name' will be the root folder of the FM, and will appear under darkmod/fms on your local filesystem. So call it something relevant to your FM. | * The ''''Repository name'''' will be the root folder of the FM, and will appear under darkmod/fms on your local filesystem. So call it something relevant to your FM. | ||
* '''Public or Private'''. This is up to you. If you choose public, your code will be visible to the internet. If you choose private, only yourself and collaborators will be able to access it. You can change it later if you want. | |||
'''IMPORTANT:''' | '''IMPORTANT:''' | ||
| Line 95: | Line 117: | ||
Browse to the repository and click the 'Code' button. A pop-up will appear with a number of options. Ensure that 'HTTPS' is selected and click the 'copy' button on the right: | Browse to the repository and click the 'Code' button. A pop-up will appear with a number of options. Ensure that 'HTTPS' is selected and click the 'copy' button on the right: | ||
[[File:Clone.jpg|500px|left]] | [[File:Clone.jpg|500px|left]] | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
Now, open up a command prompt | Now, open up a command prompt '''inside your darkmod/fms''' directory and type the following: | ||
git clone <paste the item from your clipboard> | git clone <paste the item from your clipboard> | ||
| Line 135: | Line 156: | ||
==== Open the FM folder in Visual Studio Code ==== | ==== Open the FM folder in Visual Studio Code ==== | ||
# Start VS Code and click File -> Open Folder... | |||
# Browse to darkmod\fms and click the 'tutorialfm' folder to open it | |||
You will now see something like this: | You will now see something like this: | ||
| Line 142: | Line 163: | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
* The green highlighted files indicate these files have been modified (added or updated) | * The green highlighted files indicate these files have been modified (added or updated, according to Git) | ||
* The two circled items on the left are the different 'views' in VS Code. The top (current) view is the file explorer where you'll spend most of your time. The bottom one is the 'source control' view, which we'll use to commit/push the files to Git/Github. | * The two circled items on the left are the different 'views' in VS Code. The top (current) view is the file explorer where you'll spend most of your time. The bottom one is the 'source control' view, which we'll use to commit/push the files to Git/Github. | ||
==== Commit the files to local Git repository ==== | ==== Commit the files to local Git repository ==== | ||
Even though our map | Even though our map doesn't have much in it, we can still commit it to source control. This is equivalent to the [https://git-scm.com/docs/git-commit '''git commit'''] command. | ||
# Switch to the 'version control' view in VS Code | # Switch to the 'version control' view in VS Code | ||
| Line 169: | Line 190: | ||
'''NOTE:''' At this point, you will need to authenticate with Github. Although you may be logged into the Github UI in your browser, you are not logged in on your PC. We were able to clone the repository anonymously because we made it public. Now that we want to write to it, we must authenticate. | '''NOTE:''' At this point, you will need to authenticate with Github. Although you may be logged into the Github UI in your browser, you are not logged in on your PC. We were able to clone the repository anonymously because we made it public. Now that we want to write to it, we must authenticate. | ||
You will get a pop up asking for your Github credentials, and then a request to authorize the VS Code Git extension to allow access to your Github account. Just click through until this is all done. When finished, the code will be there in your Github repo. | You will get a pop up asking for your Github credentials, and then a request to authorize the VS Code Git extension to allow access to your Github account. Just click through until this is all done ('''NOTE:''' If using [[Git_and_Github_for_Mappers#Use_SSH_for_Github_Authentication|'''SSH''']], all of this goes away). When finished, the code will be there in your Github repo. | ||
Now, if you browse to your Github repository you'll see your new files: | Now, if you browse to your Github repository you'll see your new files: | ||
| Line 182: | Line 203: | ||
For a full example of a fully developed and released mission in Github, see [https://github.com/thedarkmodcommunity/hits1 The Hare in the Snare, Part 1] in the TDM Github Community Organization. | For a full example of a fully developed and released mission in Github, see [https://github.com/thedarkmodcommunity/hits1 The Hare in the Snare, Part 1] in the TDM Github Community Organization. | ||
=== Collaboration === | === Collaboration (Advanced) === | ||
==== Introduction ==== | |||
Let's say we have two mappers who want to work on the same FM together. Without using Git, there would need to be some mechanism to share the FM files (probably by zipping and sharing .pk4 files, exporting and sharing prefab files, etc). Using Git, this process becomes much quicker and cleaner. There is one caveat however, in that it's not recommended to have multiple people working on the map file at the same time. This is a limitation of TDM and DarkRadiant, not Git. To be clear, multiple people can work on it and export parts of it (prefabs, etc), but if more than one person pushes changes, merge conflicts will likely occur in the .map file that will be next to impossible to reconcile. | |||
In our scenario, let's assume the following: | |||
* mapper A: mapping and scripting. Also owns the Git repository in Github | |||
* mapper B: models, textures, readables, etc. Basically anything but mapping. They don't own the Github repository, but they have a Github account and can be added as a collaborator. | |||
==== A word about branches ==== | |||
I haven't mentioned anything about branching in Git until now because I only wanted to introduce concepts as they are needed. However, if you are planning to collaborate you will need to understand how to use branches. The basics are enough, and you can read about it [https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/about-branches '''here'''] first. | |||
Essentially, what we are proposing is the following: | |||
* the default (also called 'main' by default) branch is protected, and nobody (not even mapper A, the owner) can push directly to it. This helps prevent screw ups and is highly recommended for collaborative projects. | |||
* both mapper A and mapper B work on their own branches | |||
* when mapper A and mapper B are finished their current task (or just want to get stuff merged), they merge their work into the default branch using something called a pull request. They can do this at any time and independently of one another (except if approvals are required - more on that later). | |||
==== Project Initialization ==== | |||
Since mapper A will be the owner of the Github project, they create the repository in Github as described above on this page. They get the map into a good enough state for others to start working on it, and they push their changes to Github. Everything is on the 'main' branch and ready to go. | |||
==== Protect the default branch ==== | |||
'''NOTE:''' this feature is only available to free accounts if you are using public repositories! | |||
As mentioned previously, it is highly recommended to protect the default branch (called 'main' by default) to avoid damaging the code (intentionally or unintentionally). You can read more about this [https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/about-branches#working-with-protected-branches here]. | |||
To protect the default branch, '''mapper A''' should follow the instructions [https://docs.github.com/en/github/administering-a-repository/defining-the-mergeability-of-pull-requests/managing-a-branch-protection-rule#creating-a-branch-protection-rule here]. | |||
The following settings are recommended at minimum: | |||
* for 'branch name pattern' choose 'main', as this will be the name of the default branch we want to protect (unless for some reason mapper A changed the name of the default branch). | |||
* tick 'require pull requests before merging' | |||
* set 'required approving reviews' to at least 1. You can set this to 2, and then both mapper A and mapper B would need to approve any merge to the default branch but his might become a hassle/hindrance. Entirely up to the mappers to decide. | |||
* tick 'Dismiss stale pull request approvals when new commits are pushed'. This will require a new approval on an existing pull request if new commits are pushed. | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:Github-branch-rule.jpg|500px|left]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
<br> | |||
==== Add a collaborator to the Github project ==== | |||
Now mapper A wants to invite mapper B to the project. Assuming mapper B also has a Github account, mapper A should then invite mapper B to the repository by following the instructions [https://docs.github.com/en/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/managing-access-to-your-personal-repositories/inviting-collaborators-to-a-personal-repository here]. | |||
Note that adding a collaborator entitles them to many permissions on the repository. See [https://docs.github.com/en/github/setting-up-and-managing-your-github-user-account/managing-user-account-settings/permission-levels-for-a-user-account-repository#collaborator-access-for-a-repository-owned-by-a-user-account here] for more information. | |||
Mapper B will now get an invite in their email to join the repository. | |||
==== Collaborator clones the repository ==== | |||
Mapper B can now clone the repository by following the instructions [[Git_and_Github_for_Mappers#Clone_the_repository_to_your_local_filesystem|above]] | |||
==== Create 'feature' branches ==== | |||
A 'feature branch' is just Git jargon to mean any branch that is being used to add new features to the codebase, so anything other than the default branch ('main' in our case), or if you are using other branches for testing or release. | |||
Both mapper A and mapper B should now do the following: | |||
To create a new branch using VS Code, do the following: | |||
# In the bottom left of VS Code, click the branch icon that says 'main' next to it. '''NOTE:''' this will always display the name of the current working branch. If you're not sure what branch you are on, just check here. | |||
# a pop up will appear. Select '+ Create new branch' | |||
# type in a name for your branch (no spaces), like 'mapper-b-work' or 'add-model' and press enter. | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:Vs-code-branch.jpg|500px|left]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
<br> | |||
You should now have a new branch in your '''local''' Git repository. Both mapper A and mapper B can now carry on and work, committing and pushing their changes to their respective remote branches in Github. | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
==== Merging your work: raising a pull request ==== | |||
Say mapper B has now finished his task and wants to merge his work. Since we protected the default branch, he can't just merge it and push to it to Github. Instead, he needs to create a '''pull request''' on Github. | |||
A pull request is essentially just a 'thing' you create that says '''"Hey, I want to merge these files from this branch into that branch. Can someone please review and approve?"''' | |||
In essence, mapper B should do the following: | |||
# Make sure his changes are pushed to Github on his branch | |||
# Raise a pull request as detailed [https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/creating-a-pull-request#creating-the-pull-request '''here'''] | |||
<br> | |||
'''NOTE:''' If you have recently pushed to Github on a branch and are logged into the UI, you will see a message like the following that makes it even easier to create a pull request: | |||
[[File:Github-create-pr.jpg|500px|thumb|left]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
==== Merging your work: approving a pull request ==== | |||
Now that mapper B has raised his pull request, mapper A can review and approve it. In our scenario, a merge requires at least 1 approval. This needs to be done by mapper A because mapper B cannot approve his own pull requests. | |||
To approve the pull request, mapper A needs to: | |||
# in the Github UI, navigate to the repository and then 'pull requests' | |||
# click on the pull request to review, and then click on 'Files changed' to review the changes | |||
# click on 'Review changes' and then 'approve'. Mapper A could instead choose to only comment, or request changes (meaning the PR can't be merged until mapper A sees and approves the desired changes). | |||
[[File:Github-approve.jpg|500px|left]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
==== Merging your work: merging a pull request ==== | |||
Now that mapper A has approved mapper B's pull request, mapper B can then merge it. To do this, follow the instructions [https://docs.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/incorporating-changes-from-a-pull-request/merging-a-pull-request#merging-a-pull-request-on-github '''here''']. | |||
==== Merging your work: quick and dirty version ==== | |||
Back when we set up our branch protection rule to protect the default branch ('main'), notice we didn't tick the box that said 'Include administrators': | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:Github-branch-rule-2.jpg|500px|left]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
What this means is that administrators of the repository (i.e. mapper A) can merge this pull request without bothering with approvals. He will get a screen like this when he views the PR: | |||
[[File:Github-merge-admin.jpg|500px|left]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
This is handy for the following scenarios: | |||
* you are working alone, but still want to protect the default branch against accidental pushes | |||
* in a collaboration scenario where mapper A wants to merge his own work without having to bother to get approvals from other collaborators | |||
==== Getting the latest version of the code ==== | |||
Now that mapper B has his changes merged, mapper A wants to get his hands on it. He has 2 choices here. He can either: | |||
# merge main into his feature branch (recommended) | |||
# merge his changes into main via pull request, update his local main branch, and then resume work on a new feature branch | |||
===== Option 1: merge from main branch ===== | |||
This is the simplest option. This will just merge changes from the main branch into the feature branch. Mapper A should: | |||
# Commit all changes to his local branch (and optionally push) | |||
# Switch to the main branch by clicking the branch icon in the bottom left of VS code (the same icon we used to create a new branch - just choose the main branch instead of creating a new one this time) | |||
# Update the local 'main' branch by clicking the 'loop' icon in the bottom left of VS Code (the same icon we used for push). This is equivalent of performing a [https://git-scm.com/docs/git-pull '''git pull'''] on the command-line. | |||
# switch back to the feature branch (again, the branch icon) | |||
# From the source control view, click the 3 dots at the top of the view, and select Branch -> Nerge branch... and then select the 'main' branch | |||
Mapper A will now have the latest changes from main, and can continue working. | |||
<br> | |||
[[File:Vs-code-merge.jpg|500px|left]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
===== Option 2: merge, pull and create new branch ===== | |||
There is no real reason to do this except if you are afraid of screwing up the merge. All the merging will be handled by Github. If you want to do this, then: | |||
# Commit, push and merge your current work as detailed above | |||
# switch to the main branch, and do a git pull by clicking the 'loop' icon in the bottom left of VS Code. This will pull the changes from mapper B and your changes from your feature branch that you just merged. | |||
# create a new branch off main and continue working. | |||
==== Implications ==== | |||
So why do all this? It seems like a hassle right? Well no, because even though it seems like you have to do a lot here, actually performing the steps takes mere seconds. Let's look at what's happening here: | |||
# Mapper A and B can both work on the same FM | |||
# Mapper B can apply his changes to the FM and push them with a couple of clicks | |||
# Mapper A can then retrieve mapper B's changes and see them in his own map with a couple of clicks | |||
# Mapper A can run DMAP and play the changes from mapper B immediately | |||
In real time, this process takes less than a minute, easily. No zipping files, no uploading/downloading from Dropbox, no extracting/copying files, etc. | |||
Another useful feature of this is mapper A or mapper B can see each others work by simply switching branches. Say mapper B is working on a new section of the map that he is going to export as a prefab later. Mapper A is getting impatient and wants to look at it. All the team needs to do is: | |||
# ensure both have committed and pushed their latest code to Github (again, a couple of seconds) | |||
# Mapper A pulls the latest code (loop icon at bottom left in VS Code) and switches to mapper B's branch | |||
# Mapper A views the work in DR, or runs DMAP and runs the map in TDM to have a look | |||
# when finished, Mapper A switches back to his own branch and resumes his work | |||
Again, all of this would only take seconds. | |||
=== Release Management === | |||
==== Features ==== | |||
Use of Github's other features such as Issues, pull requests and releases is very useful for managing the release cycle of your FM. With it, you can: | |||
# use it as your own personal bug tracker for just this particular FM. If it's public, then anyone can see it (or raise bugs if they have a Github account). You can also attach screenshots to the bug tracker entries. | |||
# use the projects feature to organise your work into columns (e.g. to do, in progress, done, etc) | |||
# host the .pk4 files for download by your beta testers | |||
# create automated changelogs (aka Release Notes) for new releases so everyone knows what's been fixed | |||
==== Setup ==== | |||
* [https://docs.github.com/en/issues/using-labels-and-milestones-to-track-work/managing-labels Add labels] to your repo that you think you might need. There are a bunch of defaults, but you may want to add more (e.g. 'gameplay', 'improvement', 'readables', etc.) | |||
* Once you have your labels, [https://docs.github.com/en/repositories/releasing-projects-on-github/automatically-generated-release-notes#configuring-automatically-generated-release-notes add the required YAML file] to your repo for generating automated release notes. | |||
==== Initial Beta Release ==== | |||
You're ready for beta and want to make the .pk4 available for your beta testers. Do the following: | |||
# Ensure all your branches are cleaned up and your main branch is up to date | |||
# Do a clean DMAP of your FM (i.e. delete all .proc, .cm, .aas files, etc. first) | |||
# Package up the .pk4. I use a Powershell script, but you can do whatever suits you. | |||
# Test the .pk4 on a clean install of TDM. I have a separate 'test' install and just delete/reinstall the .pk4 whenever I have a new version. | |||
# Once you're happy there are no issues, [https://docs.github.com/en/repositories/releasing-projects-on-github/managing-releases-in-a-repository create a release] in your Github repo. Use something like 'v1.0-beta', or 'v0.1' for the tag name to indicate it's a pre-release. | |||
# Attach the .pk4 file to the release by dropping it into the release page. You can edit the release and add it after if you forget. | |||
# Share the link to the .pk4 with your beta testers. | |||
==== Bugfix Workflow ==== | |||
Now that testers have got ahold of your beta FM, the bug reports start rolling in. | |||
This is my own personal workflow for handling these. It suits me, and helps keep me organised and makes it easy to share progress with beta testers. | |||
'''It is strongly recommended to have [[Git_and_Github_for_Mappers#Protect_the_default_branch|branch protection]] turned on for this workflow.''' This will prevent any accidental changes. | |||
Essentially what we're doing here is performing each fix in a separate pull request. The reason for this is to take advantage of the automated release notes, which expect each individual fix or change to be in its own PR. It looks like a lot of steps, but like other parts of this tutorial it becomes second nature and only takes a few seconds to perform. | |||
# Once a bug or change is identified, [https://docs.github.com/en/issues/tracking-your-work-with-issues/creating-an-issue create an issue] in your repository. For example, let's say we now have issue #8. | |||
# When you are ready to tackle the bug, make sure your local main branch is synced and create a new branch off of main in your repo just for this issue. Call the branch something like 'fix/8' to associate the branch with the actual issue you are fixing. | |||
# If you have DarkRadiant open already, '''reload the map'''. If you don't do this, DR will notify you with a pop-up message saying the underlying file has changed. | |||
# Make your changes in DR for the bugfix and test it, etc. | |||
# When you are ready to commit the fix, commit and push the new branch to Github. | |||
# Go to your Github repo in the browser and view the 'code' section. Github should notify you that a new branch has been pushed and ask you if you want to raise a pull request. Do so. | |||
# In the pull request (PR for short), make sure the title is something descriptive as it will show up in the release notes later. For example 'Fix z-fighting on castle wall'. | |||
# In the description, reference the issue you are fixing. This will associate the PR with the issue. For example, type 'fixes #8'. If you can't remember the issue number you need, just glance up at the branch name you are merging in the PR. This is why we name the branch after the issue :-) | |||
# Add a label to the pull request (e.g. 'bug'). This will categorise the fix in the automatically generated release notes. | |||
# Click 'create pull request' and then 'merge pull request'. | |||
# Before you merge, you can add a merge commit comment. Type 'fixes #8' here as well. What this does is automatically close the issue that the PR is associated with. | |||
# Click 'confirm merge' | |||
# Delete the branch | |||
# '''At this point, if you have TDM open, close it.''' If you don't, when you change branches in the next step Git will think the local map file has been modified. I think this is because TDM locks the .map file, so when you sync from Github it was not able to update it and shows it as changed from the version you just pulled from Github. | |||
# In your local git repo on your PC, change back to the 'main' branch and sync changes (or 'git pull' if using command line). | |||
# If you didn't close TDM and git is showing the .map file has changes, just revert any local changes and pull from Github. Your changes have been stored safely in Github and branch protection will prevent anything from getting lost/overwritten. | |||
==== Subsequent Beta Releases ==== | |||
This is exactly the same as the initial beta release described above, except in this case you will: | |||
* name the release (and tag) differently, say 'v0.2-beta' or 'v0.2' | |||
* When creating the release in Github, [https://docs.github.com/en/repositories/releasing-projects-on-github/automatically-generated-release-notes click the 'generate release notes' button]. This will auto-generate a changelog based on the pull requests that have been merged since the last tagged release. They should be categorised by label if you added the release YAML config mentioned in the setup. | |||
== Tips, Tricks and Advice == | |||
=== Git === | |||
==== the .gitignore file ==== | |||
the .gitignore file contains a list of filename and/or patterns to exclude from versioning. For example, you might not want to bother versioning the following: | |||
* save games | |||
* DMAP-generated files (.proc, .aas32, etc) | |||
* DR backup files | |||
* console history file | |||
* pointfiles | |||
An example .gitignore used for a FM can be found [https://github.com/thedarkmodcommunity/hits1/blob/main/.gitignore here]. | |||
=== Github === | |||
==== Use SSH for Github Authentication ==== | |||
You can use SSH for Github instead of HTTPS. It's convenient because it can make authentication easier (no prompts for usernames/passwords, etc.). There is much debate over which is 'better' or more secure. If you want to try this, you can start [https://docs.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/connecting-to-github-with-ssh/generating-a-new-ssh-key-and-adding-it-to-the-ssh-agent '''here''']. | |||
==== Delete branches after merging!!! ==== | |||
After you merge a pull request, '''always delete the branch'''. There is usually no reason to keep it, and you'll find they pile up and pollute your repository. | |||
==== Basic Collaboration Workflow ==== | |||
A suggested workflow for raising pull requests and merging goes like this: | |||
# Mapper A raises pull request and notifies Mapper B | |||
# Mapper B reviews and approves pull request | |||
# Mapper A merges pull request and deletes branch. | |||
That's it - it doesn't need to be any more complicated than that. | |||
==== Binary Files ==== | |||
Contrary to what you may read elsewhere, Git and Github handle binary files just fine. However there are a couple of things you need to be aware of, namely: | |||
* if you have files larger than 100 MB, they will be [https://docs.github.com/en/github/managing-large-files/working-with-large-files/conditions-for-large-files blocked] on push. If you are making cutscenes and brief/debrief videos, keep them under 100 MB. See [https://forums.thedarkmod.com/index.php?/topic/20904-ffmpeg-cinematics-the-only-format/&do=findComment&comment=460037 '''this forum post'''] for more information. | |||
* If you want to use larger files you can use Git LFS, but there are bandwidth and file [https://docs.github.com/en/github/managing-large-files/versioning-large-files quotas and limits]. | |||
==== Adding an Existing FM to Github ==== | |||
If you are already working on a FM and want to add it to Github now, you can do that too. Just do the following: | |||
# Make sure you have done the prerequisites listed [[Git_and_Github_for_Mappers#Tool_Setup|'''here''']]. | |||
# Create an '''empty''' Git repository by following the instructions [[Git_and_Github_for_Mappers#Create_a_new_repository|'''here''']], but '''don't add a readme or .gitignore file'''. | |||
# You will see a page that looks similar to this: | |||
[[File:Github-existing-project.jpg|500px|left]] | |||
<br clear=all> | |||
Before you start executing the commands, '''please read the following:''' | |||
* what this is doing is creating a local Git repository and then pushing it to the remote repository on Github you just created | |||
* the links it displays for the remote repository will be different from the screenshot above (they will be specific to your repository, so use those) | |||
* You need to be on the command-line inside the root of your FM folder (e.g. darkmod/fms/myfm) | |||
* these commands assume you are creating a new repository from scratch and you have no files. You do have files though, so skip the first '''echo''' command to create the readme. | |||
* instead of typing '''git add README.md''' (since we skipped creating it), add all files in the current directory by typing '''git add *''' instead | |||
* you can follow the rest of the commands as is | |||
=== VS Code === | |||
=== Other Tools === | |||
{{tutorial-editing}} | |||
Latest revision as of 22:58, 28 November 2023
Introduction
Overview
This article is about using Git and Github in the context of developing a TDM fan mission. It is important to note that Git and Github are not the same thing, rather they are used together to accomplish something: the versioning and safe storage of your work in a remote location.
There is a perception that Git is a complicated tool and isn't really needed. While it is certainly true that Git can be complicated and isn't a requirement for FM development, I will attempt to show that a basic understanding of the concepts and minimal use can have a large impact on the way you work, especially if collaboration is involved.
Using Github alongside Git goes a long way to making this easier for those new to version control concepts.
What this article isn't:
- a Git tutorial, although it will cover the basics and will be enough to get going
- an evangelism piece about the benefits of using Git over other VCS tools
What is Git and Github?
Git is a version control system (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Version_control)
Github is a cloud-based hosting service originally developed to host remote Git repositories, but has expanded to include many other services related to the software development cycle.
There are other cloud-based hosting services for Git repositories such as Gitlab and Bitbucket which offer similar functionality.
What is a Git repository?
A Git repository is a versioned collection of related files that (usually) make up a software application, or part of an application stack. In the context of this tutorial, our Git repository will only include the TDM fan mission files and nothing else.
When you create a repository on Github however, a whole bunch of other features related to the repository become available to you.
Benefits
Using Github has the following major benefits to the mapper:
- Versioning and history. Easily tell what's changed in your project, and when. Also comes in handy for fixing mistakes.
- Data loss protection. Your FM code stays in the cloud, protected by a resilient hosting platform owned and operated by Microsoft. There is almost zero risk your project can be lost
- Easier collaboration. If you work with others, using Github has many benefits that will be expanded upon in this article (for example, one-click synchronization of FM files for collaborators instead of passing .pk4 files around). See implications for more details.
- Discovery and visibility. Your FM code will be publicly available in the same place for the foreseeable future (if you choose for it to be). This makes it very easy to share, for others to find on their own, or just read later if you want to remember how you did something. Want to show someone how you wrote that script? Just send them a link!. Can't find that .ogg file you used for secrets anywhere? Just grab it!
- It's free!. See list of features available here.
Other less important features that I have found useful:
- A project board where you can create and manage work and track progress (similar to a Kanban board).
- a built-in Wiki for your project. Useful for fleshing out story ideas.
- the ability to create release artifacts. For example, you can package up your FM as a .pk4 and upload it to the project, providing a public place for others to download
- a 3D model viewer
- an image diff viewer
It is important to note that all the above features are available in the context of your FM project. Everything is in one place.
Why use a VCS and not just Google Drive/Dropbox?
Although storing your files on cloud storage protects them against data loss, there are some drawbacks:
| Feature | Git/Github | Traditional Cloud Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Resilient Cloud Hosting | yes | yes |
| Ease of file transfer | one or two clicks to synchronize, no manual compression or extracting required | manual zipping/extracting, uploading/downloading |
| Versioning | built-in | may be able to version files (e.g. Google Drive, but not a VCS and not practical unless packaged in a single file) |
| File visibility | all files easily browseable | no, especially if packaged (e.g. .pk4) |
| Discovery | public links, discoverable by anyone | no, private accounts, non-discoverable public links, may or may not be available |
| Online Collaboration | yes, via pull request | no |
Tutorial
The scope of this tutorial will:
- focus on Windows users only (although Linux users can follow along just fine - Git and VS Code are available for Linux as well)
- include the use of Visual Studio Code. The reason for using this is to demonstrate (using its Git plugin) that most Git interaction can be done without the use of the command line. If you have another preferred editor, check if it has a Git plugin and you can use that instead.
Tool Setup
Obtain a Github account
If you don't already have an account, go here and create one: https://github.com/
Install Git
You have a couple of options here, both will work:
- Git for Windows (recommended). This includes some other utilities like 'Git Bash' and a 'Git GUI' which some might find useful. Note however these are not used in the tutorial.
- Git stand-alone
First-time Git Setup
After installing Git, open a command prompt and type the following. You can put whatever you want for the values (enclose user.name in double quotes if it has a space)
git config --global user.name <your user name here> git config --global user.email <your email here>
Now do the following to confirm it worked:
git config --global --list
Install Visual Studio Code
VS Code is a very good, lightweight code editor that has become a professional standard, but is just as useful for hobbyists. I prefer it because it because of its lightweight nature and you can find well-supported plugins for pretty much anything (a lot of which are maintained by Microsoft). You can get it here: https://code.visualstudio.com/
Start using Github
Now we are ready to create a Git repository in Github. What we are going to do here is create the FM folder in Github, and then download it to our local computer. This isn't the only way to do this, but it's the easiest.
Create a new repository
NOTE: if you have an existing FM that you want to add to Github now, see Adding an Existing FM to Github.
Log into your Github account and create a new repository. Depending if this is this first time you've logged in or not, you may see different screens. Either way, you will arrive at this screen:
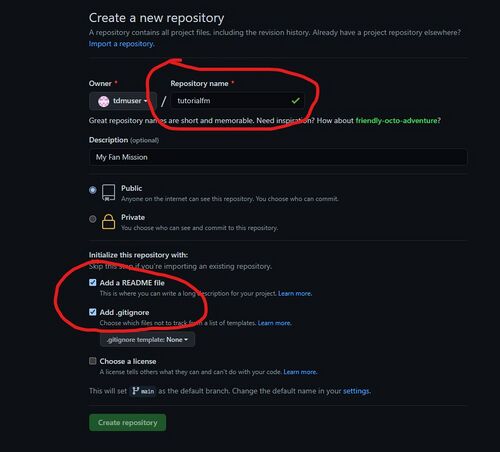
- The 'Repository name' will be the root folder of the FM, and will appear under darkmod/fms on your local filesystem. So call it something relevant to your FM.
- Public or Private. This is up to you. If you choose public, your code will be visible to the internet. If you choose private, only yourself and collaborators will be able to access it. You can change it later if you want.
IMPORTANT: Choose one or both of the following options. If you don't choose one, the repository will be empty when we 'clone' it later, and be more difficult to work with:
- README file. Readmes are markdown files that render in the Github UI automatically when you browse to a repository. Good as a 'landing page' for your project that is immediately viewable to the user.
- .gitignore. You can list file extensions in here of files that you do not want to store in Git (e.g. .proc or .cm files). If you choose this, it forces you to choose a template - just pick any one for now (e.g. VisualStudio)
When ready, click 'Create repository'
Clone the repository to your local filesystem
Now that we've created the remote Git repository for our project, we can download it ('clone' in Git parlance) to our computer. Essentially we will now have a copy (clone) of the Git repository on our local computer.
Browse to the repository and click the 'Code' button. A pop-up will appear with a number of options. Ensure that 'HTTPS' is selected and click the 'copy' button on the right:
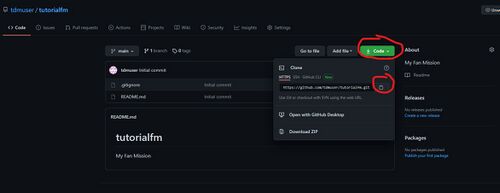
Now, open up a command prompt inside your darkmod/fms directory and type the following:
git clone <paste the item from your clipboard>
For example, using the repo in the screenshot we'd have:
git clone https://github.com/tdmuser/tutorialfm.git
Now, the repository should be present as a child of the FMs directory, named 'tutorialfm'
F:\games\darkmod_testing\fms>dir
Volume in drive F is DATA
Volume Serial Number is D43B-9D4F
Directory of F:\games\darkmod_testing\fms
23/05/2021 15:05 <DIR> .
23/05/2021 15:05 <DIR> ..
23/05/2021 15:01 45 consolehistory.dat
23/05/2021 15:01 <DIR> hareinthesnare_v1_0_3_release
23/05/2021 15:01 593 missions.tdminfo
04/04/2021 20:05 <DIR> newjob
04/04/2021 20:02 <DIR> saintlucia
04/04/2021 20:05 <DIR> stlucia
04/04/2021 20:05 <DIR> training_mission
23/05/2021 15:05 <DIR> tutorialfm
2 File(s) 638 bytes
8 Dir(s) 674,346,885,120 bytes free
Create a new Map in DarkRadiant
Now that we have our FM directory sorted, we can create a map in DR.
- Create a 'maps' folder in darkmod\fms\tutorialfm folder
- Open up DR and create a new map file
- create a simple brush on the map (or else DR won't be able to open it later)
- Click 'Save' and make sure you save it to the `darkmod\fms\tutorialfm\maps` folder. We'll call ours 'gitmap.map'
Open the FM folder in Visual Studio Code
- Start VS Code and click File -> Open Folder...
- Browse to darkmod\fms and click the 'tutorialfm' folder to open it
You will now see something like this:
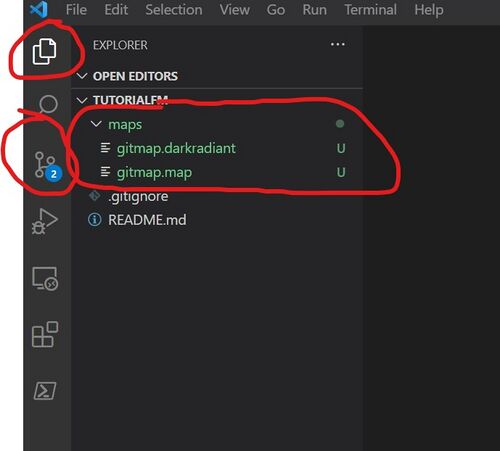
- The green highlighted files indicate these files have been modified (added or updated, according to Git)
- The two circled items on the left are the different 'views' in VS Code. The top (current) view is the file explorer where you'll spend most of your time. The bottom one is the 'source control' view, which we'll use to commit/push the files to Git/Github.
Commit the files to local Git repository
Even though our map doesn't have much in it, we can still commit it to source control. This is equivalent to the git commit command.
- Switch to the 'version control' view in VS Code
- Enter a commit message in the text box
- Click the checkmark to commit the file locally
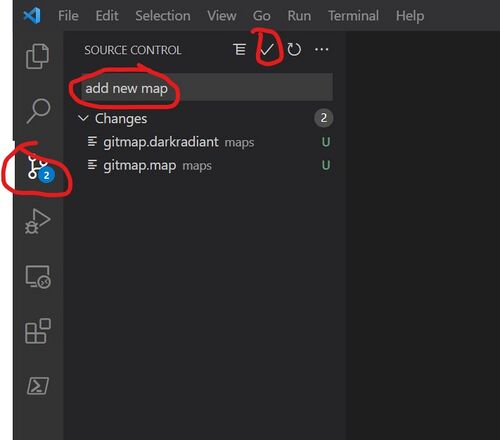
You'll notice that the green files have now disappeared from the source control view. This means that your local files are 'up to date' with those in Git repository on your computer.
Push the files to Github (remote repository)
We have committed the files to our local repository where they are now version-controlled with a commit message. But we also want to make sure we 'push' them to Github so we have a copy of our changes safely stored in the cloud. The command-line equivalent is git push.
At the bottom of your screen, you should see a 'loop' icon like so, with some arrows next to it:
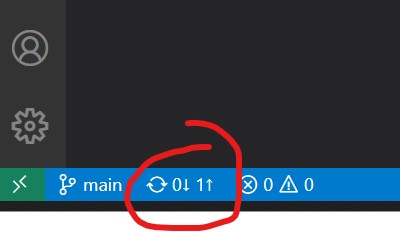
The '1' next to the up arrow means there is one commit ready to push. Click the icon to push the files to Github.
NOTE: At this point, you will need to authenticate with Github. Although you may be logged into the Github UI in your browser, you are not logged in on your PC. We were able to clone the repository anonymously because we made it public. Now that we want to write to it, we must authenticate.
You will get a pop up asking for your Github credentials, and then a request to authorize the VS Code Git extension to allow access to your Github account. Just click through until this is all done (NOTE: If using SSH, all of this goes away). When finished, the code will be there in your Github repo.
Now, if you browse to your Github repository you'll see your new files:
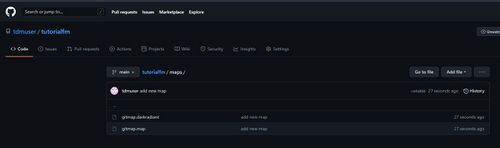
From this point onwards, any files you change, add or delete locally can be similarly committed and pushed to Github where they will be safely stored. If anything happens to your local files (deletion or your computer dies), you can re-clone the Github repository and be back to where you left off.
Running the map in TDM
You will have noticed that the FM folder we cloned from Github is now sitting within your darkmod/fms folder. This means TDM will see it as a fan mission. If you have all the required files for a FM (e.g. startingmap.txt, map file, etc) and your FM is playable, all you need to do is start TDM and install the mission in the same manner as you would if using a .pk4 file, run DMAP and off you go.
For a full example of a fully developed and released mission in Github, see The Hare in the Snare, Part 1 in the TDM Github Community Organization.
Collaboration (Advanced)
Introduction
Let's say we have two mappers who want to work on the same FM together. Without using Git, there would need to be some mechanism to share the FM files (probably by zipping and sharing .pk4 files, exporting and sharing prefab files, etc). Using Git, this process becomes much quicker and cleaner. There is one caveat however, in that it's not recommended to have multiple people working on the map file at the same time. This is a limitation of TDM and DarkRadiant, not Git. To be clear, multiple people can work on it and export parts of it (prefabs, etc), but if more than one person pushes changes, merge conflicts will likely occur in the .map file that will be next to impossible to reconcile.
In our scenario, let's assume the following:
- mapper A: mapping and scripting. Also owns the Git repository in Github
- mapper B: models, textures, readables, etc. Basically anything but mapping. They don't own the Github repository, but they have a Github account and can be added as a collaborator.
A word about branches
I haven't mentioned anything about branching in Git until now because I only wanted to introduce concepts as they are needed. However, if you are planning to collaborate you will need to understand how to use branches. The basics are enough, and you can read about it here first.
Essentially, what we are proposing is the following:
- the default (also called 'main' by default) branch is protected, and nobody (not even mapper A, the owner) can push directly to it. This helps prevent screw ups and is highly recommended for collaborative projects.
- both mapper A and mapper B work on their own branches
- when mapper A and mapper B are finished their current task (or just want to get stuff merged), they merge their work into the default branch using something called a pull request. They can do this at any time and independently of one another (except if approvals are required - more on that later).
Project Initialization
Since mapper A will be the owner of the Github project, they create the repository in Github as described above on this page. They get the map into a good enough state for others to start working on it, and they push their changes to Github. Everything is on the 'main' branch and ready to go.
Protect the default branch
NOTE: this feature is only available to free accounts if you are using public repositories!
As mentioned previously, it is highly recommended to protect the default branch (called 'main' by default) to avoid damaging the code (intentionally or unintentionally). You can read more about this here. To protect the default branch, mapper A should follow the instructions here.
The following settings are recommended at minimum:
- for 'branch name pattern' choose 'main', as this will be the name of the default branch we want to protect (unless for some reason mapper A changed the name of the default branch).
- tick 'require pull requests before merging'
- set 'required approving reviews' to at least 1. You can set this to 2, and then both mapper A and mapper B would need to approve any merge to the default branch but his might become a hassle/hindrance. Entirely up to the mappers to decide.
- tick 'Dismiss stale pull request approvals when new commits are pushed'. This will require a new approval on an existing pull request if new commits are pushed.

Add a collaborator to the Github project
Now mapper A wants to invite mapper B to the project. Assuming mapper B also has a Github account, mapper A should then invite mapper B to the repository by following the instructions here.
Note that adding a collaborator entitles them to many permissions on the repository. See here for more information.
Mapper B will now get an invite in their email to join the repository.
Collaborator clones the repository
Mapper B can now clone the repository by following the instructions above
Create 'feature' branches
A 'feature branch' is just Git jargon to mean any branch that is being used to add new features to the codebase, so anything other than the default branch ('main' in our case), or if you are using other branches for testing or release.
Both mapper A and mapper B should now do the following:
To create a new branch using VS Code, do the following:
- In the bottom left of VS Code, click the branch icon that says 'main' next to it. NOTE: this will always display the name of the current working branch. If you're not sure what branch you are on, just check here.
- a pop up will appear. Select '+ Create new branch'
- type in a name for your branch (no spaces), like 'mapper-b-work' or 'add-model' and press enter.
You should now have a new branch in your local Git repository. Both mapper A and mapper B can now carry on and work, committing and pushing their changes to their respective remote branches in Github.
Merging your work: raising a pull request
Say mapper B has now finished his task and wants to merge his work. Since we protected the default branch, he can't just merge it and push to it to Github. Instead, he needs to create a pull request on Github.
A pull request is essentially just a 'thing' you create that says "Hey, I want to merge these files from this branch into that branch. Can someone please review and approve?"
In essence, mapper B should do the following:
- Make sure his changes are pushed to Github on his branch
- Raise a pull request as detailed here
NOTE: If you have recently pushed to Github on a branch and are logged into the UI, you will see a message like the following that makes it even easier to create a pull request:
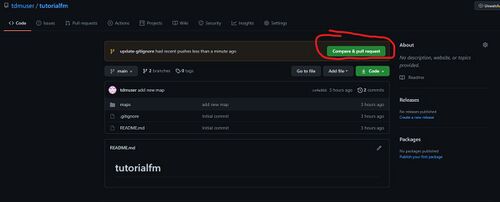
Merging your work: approving a pull request
Now that mapper B has raised his pull request, mapper A can review and approve it. In our scenario, a merge requires at least 1 approval. This needs to be done by mapper A because mapper B cannot approve his own pull requests.
To approve the pull request, mapper A needs to:
- in the Github UI, navigate to the repository and then 'pull requests'
- click on the pull request to review, and then click on 'Files changed' to review the changes
- click on 'Review changes' and then 'approve'. Mapper A could instead choose to only comment, or request changes (meaning the PR can't be merged until mapper A sees and approves the desired changes).
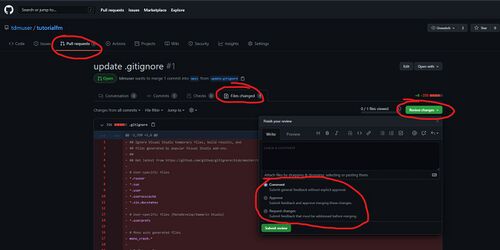
Merging your work: merging a pull request
Now that mapper A has approved mapper B's pull request, mapper B can then merge it. To do this, follow the instructions here.
Merging your work: quick and dirty version
Back when we set up our branch protection rule to protect the default branch ('main'), notice we didn't tick the box that said 'Include administrators':
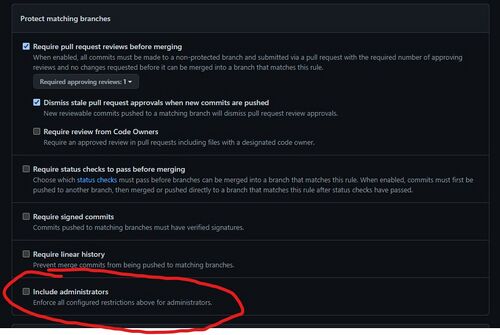
What this means is that administrators of the repository (i.e. mapper A) can merge this pull request without bothering with approvals. He will get a screen like this when he views the PR:
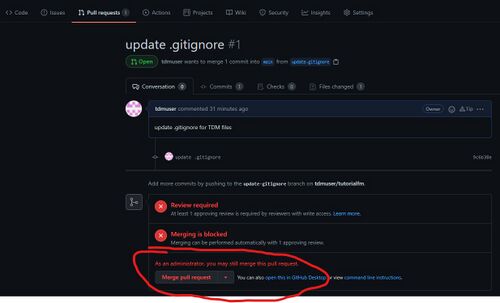
This is handy for the following scenarios:
- you are working alone, but still want to protect the default branch against accidental pushes
- in a collaboration scenario where mapper A wants to merge his own work without having to bother to get approvals from other collaborators
Getting the latest version of the code
Now that mapper B has his changes merged, mapper A wants to get his hands on it. He has 2 choices here. He can either:
- merge main into his feature branch (recommended)
- merge his changes into main via pull request, update his local main branch, and then resume work on a new feature branch
Option 1: merge from main branch
This is the simplest option. This will just merge changes from the main branch into the feature branch. Mapper A should:
- Commit all changes to his local branch (and optionally push)
- Switch to the main branch by clicking the branch icon in the bottom left of VS code (the same icon we used to create a new branch - just choose the main branch instead of creating a new one this time)
- Update the local 'main' branch by clicking the 'loop' icon in the bottom left of VS Code (the same icon we used for push). This is equivalent of performing a git pull on the command-line.
- switch back to the feature branch (again, the branch icon)
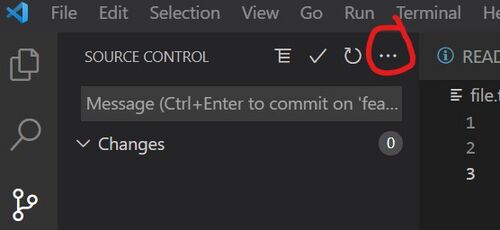
- From the source control view, click the 3 dots at the top of the view, and select Branch -> Nerge branch... and then select the 'main' branch
Mapper A will now have the latest changes from main, and can continue working.
Option 2: merge, pull and create new branch
There is no real reason to do this except if you are afraid of screwing up the merge. All the merging will be handled by Github. If you want to do this, then:
- Commit, push and merge your current work as detailed above
- switch to the main branch, and do a git pull by clicking the 'loop' icon in the bottom left of VS Code. This will pull the changes from mapper B and your changes from your feature branch that you just merged.
- create a new branch off main and continue working.
Implications
So why do all this? It seems like a hassle right? Well no, because even though it seems like you have to do a lot here, actually performing the steps takes mere seconds. Let's look at what's happening here:
- Mapper A and B can both work on the same FM
- Mapper B can apply his changes to the FM and push them with a couple of clicks
- Mapper A can then retrieve mapper B's changes and see them in his own map with a couple of clicks
- Mapper A can run DMAP and play the changes from mapper B immediately
In real time, this process takes less than a minute, easily. No zipping files, no uploading/downloading from Dropbox, no extracting/copying files, etc.
Another useful feature of this is mapper A or mapper B can see each others work by simply switching branches. Say mapper B is working on a new section of the map that he is going to export as a prefab later. Mapper A is getting impatient and wants to look at it. All the team needs to do is:
- ensure both have committed and pushed their latest code to Github (again, a couple of seconds)
- Mapper A pulls the latest code (loop icon at bottom left in VS Code) and switches to mapper B's branch
- Mapper A views the work in DR, or runs DMAP and runs the map in TDM to have a look
- when finished, Mapper A switches back to his own branch and resumes his work
Again, all of this would only take seconds.
Release Management
Features
Use of Github's other features such as Issues, pull requests and releases is very useful for managing the release cycle of your FM. With it, you can:
- use it as your own personal bug tracker for just this particular FM. If it's public, then anyone can see it (or raise bugs if they have a Github account). You can also attach screenshots to the bug tracker entries.
- use the projects feature to organise your work into columns (e.g. to do, in progress, done, etc)
- host the .pk4 files for download by your beta testers
- create automated changelogs (aka Release Notes) for new releases so everyone knows what's been fixed
Setup
- Add labels to your repo that you think you might need. There are a bunch of defaults, but you may want to add more (e.g. 'gameplay', 'improvement', 'readables', etc.)
- Once you have your labels, add the required YAML file to your repo for generating automated release notes.
Initial Beta Release
You're ready for beta and want to make the .pk4 available for your beta testers. Do the following:
- Ensure all your branches are cleaned up and your main branch is up to date
- Do a clean DMAP of your FM (i.e. delete all .proc, .cm, .aas files, etc. first)
- Package up the .pk4. I use a Powershell script, but you can do whatever suits you.
- Test the .pk4 on a clean install of TDM. I have a separate 'test' install and just delete/reinstall the .pk4 whenever I have a new version.
- Once you're happy there are no issues, create a release in your Github repo. Use something like 'v1.0-beta', or 'v0.1' for the tag name to indicate it's a pre-release.
- Attach the .pk4 file to the release by dropping it into the release page. You can edit the release and add it after if you forget.
- Share the link to the .pk4 with your beta testers.
Bugfix Workflow
Now that testers have got ahold of your beta FM, the bug reports start rolling in. This is my own personal workflow for handling these. It suits me, and helps keep me organised and makes it easy to share progress with beta testers.
It is strongly recommended to have branch protection turned on for this workflow. This will prevent any accidental changes.
Essentially what we're doing here is performing each fix in a separate pull request. The reason for this is to take advantage of the automated release notes, which expect each individual fix or change to be in its own PR. It looks like a lot of steps, but like other parts of this tutorial it becomes second nature and only takes a few seconds to perform.
- Once a bug or change is identified, create an issue in your repository. For example, let's say we now have issue #8.
- When you are ready to tackle the bug, make sure your local main branch is synced and create a new branch off of main in your repo just for this issue. Call the branch something like 'fix/8' to associate the branch with the actual issue you are fixing.
- If you have DarkRadiant open already, reload the map. If you don't do this, DR will notify you with a pop-up message saying the underlying file has changed.
- Make your changes in DR for the bugfix and test it, etc.
- When you are ready to commit the fix, commit and push the new branch to Github.
- Go to your Github repo in the browser and view the 'code' section. Github should notify you that a new branch has been pushed and ask you if you want to raise a pull request. Do so.
- In the pull request (PR for short), make sure the title is something descriptive as it will show up in the release notes later. For example 'Fix z-fighting on castle wall'.
- In the description, reference the issue you are fixing. This will associate the PR with the issue. For example, type 'fixes #8'. If you can't remember the issue number you need, just glance up at the branch name you are merging in the PR. This is why we name the branch after the issue :-)
- Add a label to the pull request (e.g. 'bug'). This will categorise the fix in the automatically generated release notes.
- Click 'create pull request' and then 'merge pull request'.
- Before you merge, you can add a merge commit comment. Type 'fixes #8' here as well. What this does is automatically close the issue that the PR is associated with.
- Click 'confirm merge'
- Delete the branch
- At this point, if you have TDM open, close it. If you don't, when you change branches in the next step Git will think the local map file has been modified. I think this is because TDM locks the .map file, so when you sync from Github it was not able to update it and shows it as changed from the version you just pulled from Github.
- In your local git repo on your PC, change back to the 'main' branch and sync changes (or 'git pull' if using command line).
- If you didn't close TDM and git is showing the .map file has changes, just revert any local changes and pull from Github. Your changes have been stored safely in Github and branch protection will prevent anything from getting lost/overwritten.
Subsequent Beta Releases
This is exactly the same as the initial beta release described above, except in this case you will:
- name the release (and tag) differently, say 'v0.2-beta' or 'v0.2'
- When creating the release in Github, click the 'generate release notes' button. This will auto-generate a changelog based on the pull requests that have been merged since the last tagged release. They should be categorised by label if you added the release YAML config mentioned in the setup.
Tips, Tricks and Advice
Git
the .gitignore file
the .gitignore file contains a list of filename and/or patterns to exclude from versioning. For example, you might not want to bother versioning the following:
- save games
- DMAP-generated files (.proc, .aas32, etc)
- DR backup files
- console history file
- pointfiles
An example .gitignore used for a FM can be found here.
Github
Use SSH for Github Authentication
You can use SSH for Github instead of HTTPS. It's convenient because it can make authentication easier (no prompts for usernames/passwords, etc.). There is much debate over which is 'better' or more secure. If you want to try this, you can start here.
Delete branches after merging!!!
After you merge a pull request, always delete the branch. There is usually no reason to keep it, and you'll find they pile up and pollute your repository.
Basic Collaboration Workflow
A suggested workflow for raising pull requests and merging goes like this:
- Mapper A raises pull request and notifies Mapper B
- Mapper B reviews and approves pull request
- Mapper A merges pull request and deletes branch.
That's it - it doesn't need to be any more complicated than that.
Binary Files
Contrary to what you may read elsewhere, Git and Github handle binary files just fine. However there are a couple of things you need to be aware of, namely:
- if you have files larger than 100 MB, they will be blocked on push. If you are making cutscenes and brief/debrief videos, keep them under 100 MB. See this forum post for more information.
- If you want to use larger files you can use Git LFS, but there are bandwidth and file quotas and limits.
Adding an Existing FM to Github
If you are already working on a FM and want to add it to Github now, you can do that too. Just do the following:
- Make sure you have done the prerequisites listed here.
- Create an empty Git repository by following the instructions here, but don't add a readme or .gitignore file.
- You will see a page that looks similar to this:
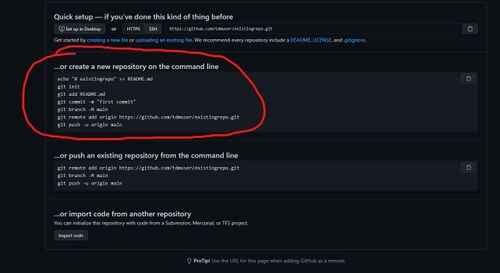
Before you start executing the commands, please read the following:
- what this is doing is creating a local Git repository and then pushing it to the remote repository on Github you just created
- the links it displays for the remote repository will be different from the screenshot above (they will be specific to your repository, so use those)
- You need to be on the command-line inside the root of your FM folder (e.g. darkmod/fms/myfm)
- these commands assume you are creating a new repository from scratch and you have no files. You do have files though, so skip the first echo command to create the readme.
- instead of typing git add README.md (since we skipped creating it), add all files in the current directory by typing git add * instead
- you can follow the rest of the commands as is